Introduction
As agentic AI systems become more integrated into our daily workflows, ensuring their safety and reliability is more critical than ever. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has significantly improved AI accuracy, but it’s not foolproof. To protect against risks like data leakage and false information, a robust guardrail system is necessary. This guide explores a three-layer guardrail structure, offering a blueprint for building trustworthy AI that you can depend on in 2026 and beyond.Understanding the Three-Layer Guardrail in Agentic RAG Systems
A three-layer guardrail acts as a comprehensive defense mechanism for your agentic RAG systems. Each layer performs specific safety checks, working together to create a secure environment for your generative AI applications. This multi-layered approach helps mitigate a wide range of risks, from inaccurate outputs to malicious attacks.By implementing these layers, you can protect your AI systems against vulnerabilities like prompt injection, data exfiltration, and reputational damage. Let’s explore the foundational concepts of RAG and why these advanced safety measures are becoming a standard practice.Overview of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and AgenticOps
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that enhances the capabilities of an AI agent by connecting it to external data sources. Instead of relying solely on its training data, a RAG system can retrieve relevant, up-to-date information to answer your questions more accurately. This dramatically improves what the AI “knows” and reduces the chances of it making things up.Agentic RAG takes this a step further. While a standard RAG system retrieves and presents information, an agentic RAG system can reason, decompose complex tasks, and take action. It’s the difference between an AI that can find a recipe and an AI that can also check your inventory and add missing ingredients to a shopping list.This advanced capability is managed through a practice called AgenticOps, which focuses on the entire lifecycle of developing, deploying, and maintaining these intelligent agents. AgenticOps ensures that the AI agent performs its tasks reliably and efficiently, optimizing everything from data retrieval to response times.To implement these guardrails effectively, combine this strategy with your organisation’s existing AI development services to ensure that safety mechanisms are integrated into your deployment lifecycle.Why Multi-Layered Guardrails Matter in 2026
As we look toward 2026, the stakes for AI safety are higher than ever. AI systems are no longer just experimental tools; they are integral parts of business operations, facing real-world vulnerabilities and regulatory scrutiny. A single incident, whether it’s an AI providing harmful advice or leaking sensitive data, can lead to significant financial loss and reputational damage.Incidents like Google’s Bard error causing a $100 billion stock drop or Slack AI suffering from data exfiltration highlight the urgent need for robust protection. Furthermore, new regulatory requirements, such as the EU AI Act, mandate strict controls on high-risk AI systems, making guardrails a matter of compliance, not just a best practice.A multi-layered guardrail is designed to address these modern challenges. While no system is perfect, a three-layer defense provides a sufficient and pragmatic approach for production-level AI safety. It creates defense-in-depth, making it significantly harder for bad outputs or security breaches to occur, ensuring your AI systems operate safely and responsibly.Key Differences Between Traditional AI Safety and Agentic RAG Guardrails
Traditional AI safety often focuses on broad concepts like model alignment, ensuring an AI’s goals are aligned with human values during its initial training. While important, this approach is not enough for dynamic, real-world applications. Agentic RAG guardrails offer a more practical, real-time solution by implementing checks at every stage of the AI’s operation.Instead of a one-time training solution, guardrails provide continuous oversight. They are less about the AI’s internal “morality” and more about enforcing explicit rules and policies on its inputs and outputs. This shift makes safety a tangible, measurable part of the AI pipeline.Key differences include:- Layered Defense: Agentic RAG guardrails use a multi-layer system (input, process, output) rather than a single alignment strategy.
- Real-Time Detection: They actively scan for issues like PII, toxicity, and hallucinations as they happen.
- Specificity: Guardrails are tailored to specific risks and use cases, such as blocking certain topics or validating data formats.
- Action-Oriented: They are designed for agents that take action, providing checks before, during, and after a task is performed.
The Structure of a Three-Layer Guardrail
The strength of a three-layer guardrail lies in its structured, defense-in-depth approach. Think of it as a security checkpoint for your agentic RAG system, where each layer is responsible for spotting different types of problems. This schema provides a comprehensive blueprint for protecting your AI systems from common pitfalls.This structure ensures that potential issues are caught at multiple points in the pipeline, from the moment a user query is received to the final delivery of the AI’s response. Let’s break down what each of these three critical layers does.First Layer: Input Validation and Filtering
The first layer serves as the initial line of defense for your AI systems. Its job is to perform input sanitization on every user query before it’s processed. This foundational guardrail uses fast, rule-based checks to filter out obvious violations and malicious attempts right at the entry point.These validators are deterministic and operate with extremely low latency (often under 10 milliseconds), making them highly efficient. They catch clear-cut problems without slowing down the user experience. By handling these issues upfront, this layer prevents harmful or malformed data from ever reaching the core of your AI.This first line of defense is crucial for system reliability and includes:- PII Detection: Using patterns (regex) to find and block personally identifiable information like social security numbers or credit card details.
- Keyword Blocklists: Preventing queries that contain offensive language, competitor mentions, or restricted topics.
- Format Checking: Ensuring the user query meets required formats, such as length limits or allowed characters.
- Jailbreak Detection: Recognizing and blocking common prompts designed to manipulate the AI.
Second Layer: Data Integrity and Context Protection
Once an input has passed the first layer, the second layer focuses on protecting data integrity and maintaining conversational context. This layer uses machine learning (ML) classifiers to detect nuanced issues that simple rules would miss. It acts as a more intelligent filter, understanding the context of a conversation.These ML models can identify subtle toxicity, bias, or off-topic questions that may not contain specific blocked keywords but are still inappropriate. For example, it can determine if a conversation is drifting into a domain the AI agent is not authorized to discuss, such as giving financial advice when it’s only supposed to handle customer support.This layer is critical for mitigating risks related to brand safety and user trust. By analyzing metadata and conversational flow, it ensures the AI agent doesn’t process or expose sensitive data inappropriately and stays on its designated topic, providing relevant and safe responses.Third Layer: Output Monitoring for Hallucination Reduction
The third and final layer is dedicated to monitoring the generated content before it reaches the user. This is where you directly tackle the problem of hallucination—when an AI generates plausible but factually incorrect information. This layer uses another powerful Large Language Model (LLM) to validate the AI’s response for accuracy and coherence.This validation is the most computationally intensive but also the most powerful. It checks if the generated content is “grounded” in the source documents retrieved by the RAG system. It also ensures the response aligns with complex ethical guidelines or company policies, something rule-based checks cannot do.By implementing robust observability and monitoring at this stage, you can track metrics related to factual consistency and intent alignment. This layer is your final quality check to ensure the information your users receive is trustworthy.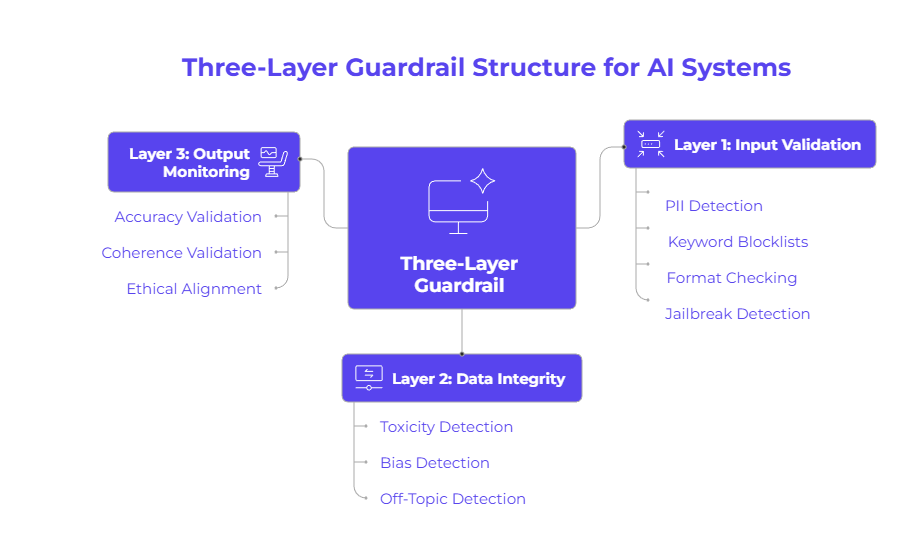
Benefits of Implementing a Three-Layer Guardrail
Adopting a three-layer guardrail offers significant benefits for any organization deploying AI systems. The most immediate advantage is a dramatic improvement in reliability and security. By creating multiple checkpoints, you build a resilient system that is far less susceptible to common AI vulnerabilities.This approach also fosters greater trust and transparency. When you can demonstrate that robust safety measures are in place, stakeholders, customers, and regulators are more likely to have confidence in your AI. Let’s look at some of these key benefits in more detail.Enhancing Reliability and Trust with Zero-Trust AI Principles
The three-layer guardrail model aligns perfectly with the principles of Zero-Trust AI. The core idea behind zero-trust is “never trust, always verify.” Instead of assuming any part of your system is secure, you enforce strict authentication and authorization at every step of the pipeline.Applying this to your AI systems means you don’t blindly trust user inputs or the AI’s generated responses. The first layer acts as a foundational guardrail, verifying inputs before they enter your system. The second and third layers continue this verification process, checking the AI’s reasoning and its final output.This continuous verification enhances system reliability by catching errors and malicious behavior at multiple points. It ensures that every action taken by the AI is scrutinized, building a trustworthy environment where you can have confidence that the system is operating as intended and within its designated boundaries.Minimizing Risk of Hallucinations in AgenticOps Workflows
Hallucinations remain one of the biggest challenges for any RAG system. A three-layer guardrail provides a powerful toolkit for minimizing this risk within your AgenticOps workflows. While the RAG process itself improves accuracy, the guardrails add critical safety checks to catch any falsehoods that slip through.The third layer, output monitoring, is specifically designed for this purpose. It uses an LLM to perform a final review of the generated content, comparing it against the retrieved source material. This step forces the model to ground its claims in evidence, preventing it from generating plausible-sounding fiction.Here’s how this layered approach helps reduce hallucinations:- Groundedness Checking: Ensures the response aligns with the facts present in the source documents.
- Evidence-Based Construction: Requires the AI to cite its sources for every claim it makes.
- Self-Critique Prompts: Encourages the model to review and revise its own draft for logical gaps or unsupported claims.
- Factual Consistency Checks: Scans the response for internal contradictions.
Increasing Transparency for Enterprise Audits
In an enterprise environment, transparency is not just a nice-to-have; it’s a requirement for compliance and governance. A three-layer guardrail system generates a wealth of data that can be used for audits and continuous improvement. Every time a guardrail is triggered, it creates a log entry.This log provides a clear and detailed trail of how the AI system is making decisions and what content it is blocking. You can use these metrics and analytics to demonstrate to auditors and regulators that you have effective controls in place to manage AI risk.This level of observability allows you to track false positive rates (when a guardrail blocks legitimate content) and false negative rates (when it misses a violation). This data-driven approach to AI safety makes it easier to refine your policies, improve your guardrails, and maintain a high level of transparency across your entire enterprise deployment.Technologies for Guardrail Deployment in Agentic RAG Pipelines
Implementing a three-layer guardrail requires a combination of technologies working together within your agentic RAG pipeline. You can’t rely on a single tool; instead, you need a stack that includes rule-based engines, machine learning models, and large language models for validation.Fortunately, the ecosystem of tools for AI safety is rapidly maturing. From open-source frameworks to managed services, you have options for building, deploying, and monitoring these critical safeguards. Let’s examine some of the key technologies you can use.Large Model Program (LMP) Integration Strategies
Integrating guardrails into your Large Model Program (LMP) is a crucial step. This involves treating your LLM not as a black box but as a component within a larger, structured pipeline. A well-defined schema or blueprint is essential for ensuring that guardrails can interact with the LLM at the right moments.One popular approach is to use an orchestration platform like NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails. This type of tool allows you to define your safety policies in a simple configuration file and then applies them to the LLM pipeline. You can specify different guardrails for input, output, and even for internal conversational turns.This integration strategy allows you to chain different models together. For example, your main LLM might generate a response, which is then passed to a specialized safety LLM (like Llama 3.1 NemoGuard 8B ContentSafety) for validation. This modular approach makes your LMP more robust and easier to manage.For deeper insights into current software and AI trends that inform guardrail strategies, explore our Techwink blog on AI & software trends.Automation Tools for Continuous Guardrail Reinforcement
Your guardrails should not be static. The landscape of AI threats is constantly evolving, so your safety checks must adapt. Automation tools are essential for achieving the continuous improvement needed to keep your guardrails effective over time.These tools help with the ongoing monitoring and reinforcement of your safety policies. By automating the analysis of guardrail performance, you can quickly identify weaknesses and refine your rules without manual intervention. This creates a feedback loop that strengthens your defenses.Here are some key automation strategies:- Automated Logging: Automatically log all guardrail triggers and collect metrics on their performance.
- Anomaly Detection: Use automation to detect unusual patterns in user queries or AI responses that might indicate a new threat.
- A/B Testing: Automatically test new guardrail rules against existing ones to measure their effectiveness.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Integrate guardrail updates into your existing CI/CD pipeline for seamless deployment.
Monitoring Solutions to Track Guardrail Effectiveness
You can’t improve what you can’t measure. Effective monitoring and observability solutions are a cornerstone of any successful guardrail deployment. These tools give you the visibility you need to understand how your guardrails are performing in a production environment.Monitoring solutions go beyond simple logging. They provide dashboards, analytics, and alerting capabilities that turn raw data into actionable insights. You can track key metrics like the latency introduced by each guardrail, the rate of false positives, and the types of threats being detected most frequently.This deep level of insight is a best practice for enterprise systems. It allows you to prove the effectiveness of your safety measures during audits and helps you make informed decisions about where to invest in further improvements. With the right monitoring in place, you can ensure your guardrails are not only working but are also optimized for performance and accuracy.Best Practices for Enterprise-Scale Guardrail Implementation
Deploying a guardrail system in a large enterprise requires more than just the right technology. It demands a strategic approach that considers agentic AI governance, compliance, and collaboration across teams. Following established best practices can help you navigate the complexities of an enterprise-scale implementation.A successful deployment is one that is effective, scalable, and sustainable. It should integrate seamlessly with existing workflows and meet the stringent requirements of your industry. Here are some key practices to guide your implementation.Aligning Guardrail Design with AgenticOps Objectives
Your guardrails should be enablers, not blockers. A common pitfall is designing safety measures that are so restrictive they hinder the AI’s ability to perform its intended workflow. To avoid this, it’s crucial to align your guardrail design directly with your AgenticOps objectives.Start by clearly defining what you want your AI agent to achieve. Is its purpose to answer customer questions, summarize documents, or automate a business process? Once you know the objectives, you can design guardrails that support those goals while mitigating the specific risks involved.This alignment ensures a healthy balance between safety and functionality. Here’s how to achieve it:- Define Use Cases: Clearly map out the specific tasks the AI will perform.
- Risk-Based Routing: Apply stricter guardrails only to high-risk queries, allowing low-risk workflows to proceed with minimal friction.
- Contextual Policies: Create policies that understand the context of a task rather than applying a blanket rule to everything.
- Measure Business Impact: Track metrics to ensure guardrails are not negatively impacting key performance indicators like customer satisfaction or task completion rates.
Collaboration Between Security and LMP Engineering Teams
Building effective guardrails is a team sport. It requires close collaboration between your security teams and your Large Model Program (LMP) engineering teams. These groups often have different priorities and perspectives, but their combined expertise is essential for a successful outcome.Security teams are experts in identifying threats, understanding compliance requirements, and designing robust controls. LMP engineering teams, on the other hand, have deep knowledge of the AI models, their capabilities, and the technical constraints of the pipeline. When these teams work together, they can create guardrails that are both effective and practical.This collaboration should start early in the design process and continue throughout the lifecycle of the AI application. Regular communication, shared goals, and a mutual understanding of the risks and trade-offs will lead to a much stronger and more sustainable AI governance framework.Compliance, Scalability, and Maintenance Considerations
When deploying guardrails at an enterprise scale, you must plan for the long term. Three key considerations are compliance, scalability, and maintenance. Your guardrail system must be able to meet current and future regulatory requirements. This means keeping it updated as laws like the EU AI Act evolve.Scalability is another critical factor. As you deploy more AI agents or as user traffic grows, your guardrail pipeline must be able to handle the increased load without becoming a bottleneck. This often involves choosing technologies that can be scaled horizontally and optimizing your rules for performance.Finally, maintenance cannot be an afterthought. Your guardrail system will require regular updates, tuning, and monitoring. You need a clear plan for who is responsible for this maintenance and what processes they will follow. A well-maintained system is essential for mitigating risks effectively over the long run.Common Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
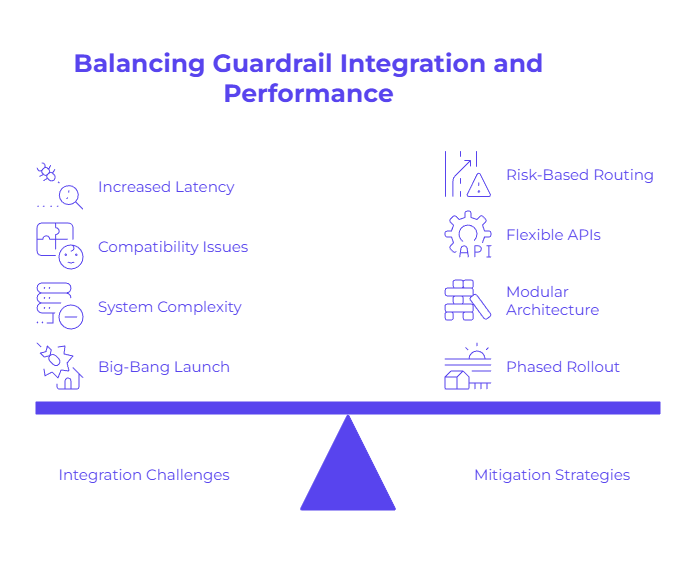
While the benefits of a three-layer guardrail are clear, implementing one for your agentic RAG system is not without its challenges. You may face technical hurdles related to integration, performance trade-offs, and the need to adapt to new vulnerabilities.Anticipating these challenges is the first step toward overcoming them. By having clear mitigation strategies in place, you can ensure a smoother and more successful deployment. Let’s explore some of the most common obstacles and how you can address them.Integrating Guardrails into Existing RAG Architectures
Integrating a new guardrail system into an existing RAG architecture can be complex. You might have a finely tuned pipeline, and adding new components can risk disrupting it. The key challenge is to add the necessary safety layers without breaking what already works.A well-designed blueprint for your agentic RAG pipeline can make this integration much easier. Using modular components and standardized APIs allows you to insert guardrails at the appropriate stages—input, process, and output—with minimal disruption.Here are some common integration challenges and how to mitigate them:- Increased Latency: Adding more checks can slow down response times. Mitigate this by using risk-based routing and parallel processing.
- Compatibility Issues: New tools may not be compatible with your existing stack. Mitigate this by choosing tools with flexible APIs.
- Complexity: The overall system becomes more complex. Mitigate this with clear documentation and a modular architecture.
- Phased Rollout: Instead of a big-bang launch, roll out guardrails layer by layer to identify and fix issues incrementally.
Balancing Performance, Security, and User Experience
One of the most delicate balancing acts in AI safety is managing the trade-offs between performance, security, and user experience. Overly aggressive security checks can introduce significant latency, leading to a slow and frustrating experience for users. However, prioritizing speed above all else can expose you to unacceptable risks.The solution is not to choose one over the other but to find a strategic balance. This is where risk-based routing becomes invaluable. By classifying each query based on its potential risk, you can apply the full, synchronous three-layer validation only when absolutely necessary, such as for financial or medical advice.For low-risk queries, you can use a lighter touch, perhaps running validation asynchronously while streaming the response to the user. By tracking performance metrics like latency alongside security metrics, you can continuously tune this balance to meet the specific needs of your application and the expectations of your users.Adapting to Evolving AgenticOps Threats in 2026
The world of AI threats is not static. Adversaries are constantly developing new techniques for prompt injection, data exfiltration, and other forms of misuse. What works as a defense today may not be effective tomorrow. Therefore, adaptability and continuous improvement must be at the core of your AgenticOps security strategy.Your guardrail system needs to be designed for change. This means using flexible tools that can be easily updated with new rules and models. It also means fostering a culture of vigilance, where your teams are actively looking for new threats and testing your defenses against them.Tools like NVIDIA Garak, an open-source scanner for LLM vulnerabilities, can help you proactively identify weaknesses in your system. By regularly testing your AI agents against the latest known jailbreaks and attack vectors, you can adapt your defenses before a real incident occurs, ensuring your system remains secure against the evolving threats of 2026.Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing a three-layer guardrail for Agentic RAG is not just a best practice; it’s essential for navigating the evolving landscape of AI systems in 2026. By prioritizing input validation, ensuring data integrity, and monitoring output effectively, organizations can significantly mitigate risks associated with hallucinations while enhancing reliability and transparency. As we move forward, aligning these guardrail strategies with AgenticOps objectives will be crucial. Embracing this structured approach will not only protect your systems but also instill trust in users and stakeholders alike. If you’re ready to strengthen your AI safety protocols, reach out to our experts for a free consultation today!Contents
Frequently Asked Questions
Most frequent questions and answers
The three layers of an AI guardrail for AI systems provide defense-in-depth. The first layer is input validation to filter user queries. The second layer protects data integrity during processing. The third layer is output monitoring to check for issues like hallucination before delivering the response.
To secure agentic RAG in an enterprise, you must implement multi-layered security guardrails. This involves aligning with compliance requirements, establishing continuous monitoring and logging for audits, and fostering collaboration between security and engineering teams to manage risks effectively.
A standard RAG system retrieves information to answer a query. An agentic RAG system takes it a step further; the AI agent can also reason, decompose tasks, and execute a workflow. It moves from simply providing information to taking action with greater precision.
You can prevent hallucinations in autonomous AI agents by implementing robust output monitoring. This involves using safety checks like groundedness detection, which verifies the AI’s response against source data, and self-critique mechanisms that force the model to revise unsupported claims before finalizing its answer.



