Introduction
Welcome to 2026, a pivotal year for enterprise AI. The landscape of generative AI has moved beyond experimentation into production-critical systems, and with this shift comes new responsibilities. For CTOs, ensuring the safety and compliance of these powerful tools is no longer optional. This guide explores why AI safety guardrails in 2026 are crucial for your Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architectures and how you can implement them to drive innovation securely and maintain trust in your organization’s AI initiatives.
To deepen your understanding of emerging enterprise AI patterns, see this overview on
👉 https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/generative-ai
👉 https://www.gartner.com/en/topics/artificial-intelligence
Understanding the 2026 Mandate: The End of “Black Box” AI for CTOs
Navigating the 2026 regulatory landscape means moving away from opaque AI systems towards transparent, accountable architectures. This shift fundamentally alters how CTOs strategize around information access, highlighting the need for robust governance frameworks and continuous monitoring. The focus now lies on ensuring data quality and safeguarding sensitive information. Integrating RAG systems fosters real-time feedback loops and human oversight, crucial for risk management. By grounding outputs and validating data sources, organizations can maintain user satisfaction while meeting regulatory requirements, ultimately enhancing their competitive advantage in an evolving landscape of AI technology.
How the EU AI Act and Global Regulations Reshaped Enterprise AI in 2026
Global regulations like the EU AI Act have reshaped enterprise AI, making compliance a top priority for CTOs. These rules require accountability, transparency, and strong risk management to protect users and ensure predictable AI behavior, especially in critical industries.
To comply with regulations for RAG models in 2026, integrate AI safety guardrails from the start. Establish clear governance that documents every step—from data sourcing to deployment—and demonstrate fairness, security, and reliability.
Major cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, and Google now offer native tooling for responsible AI, secure embeddings, and governed RAG pipelines:
This proactive approach not only avoids penalties but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders. Aligning your AI strategy with global standards positions your organization as a responsible leader in transparent AI.
The Shift from Opaque Models to Transparent, Auditable AI Workflows
The push for regulatory compliance is driving a shift away from opaque AI systems. Previously, many language models operated as black boxes, making their decisions hard to understand and increasing the risk of errors or bias.
Now, the focus is on transparent, auditable AI workflows. Every step—from data retrieval to final output—must be traceable. Comprehensive audit trails show exactly what information the model used, providing clear insight into its behavior.
This move toward transparency isn’t just about compliance; it’s about building trustworthy AI. Explaining and verifying AI outputs increases reliability and user confidence. For CTOs, embracing this shift is essential for scaling AI successfully.
Regulatory Triggers CTOs Must Track When Deploying RAG Systems
When integrating RAG systems into enterprise workflows, be alert to regulatory triggers that may classify your AI as high-risk. Proactive risk management is key to navigating complex compliance requirements.
Identifying these triggers ensures you design secure, compliant systems from the start. Focus on controlling access to sensitive data, preventing data leakage, and grounding AI outputs in verified sources. Security must be built into your RAG systems to meet 2026 standards.
Critical triggers for CTOs include:
- Regulated Industries: Deploying RAG in finance, healthcare, or legal sectors brings higher scrutiny.
- Sensitive Data Access: Handling PII or confidential information subjects your system to strict data protection laws.
- Decision-Making Impact: AI affecting major decisions—like hiring or credit scoring—must meet rigorous fairness and transparency rules.
- Public-Facing Applications: Customer-facing bots require oversight to prevent misinformation and harmful content.
Why AI Safety Guardrails Are Now Essential for RAG Architectures
As RAG architectures become central to enterprise AI, deploying them without proper safeguards is a recipe for disaster. RAG guardrails are no longer a “nice-to-have” feature; they are a fundamental requirement for secure and responsible AI deployment. These guardrails act as the essential safety net for your systems.
Leading research from IBM highlights that ungoverned generative systems increase breach probability by over 40%.
The AI safety guardrails of 2026 ensure that your RAG models produce accurate, compliant, and reliable results. Let’s look at the specific risks of unchecked RAG systems, the governance challenges you’ll face, and how you can strike the right balance between innovation and safety.
The Risks of Unchecked Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Enterprise Environments
Deploying RAG systems without strong guardrails puts your organization at risk. Unchecked AI can become a liability, leading to legal issues, reputational harm, and loss of trust. The quality of your AI’s output depends on its retrieval process.
Without safeguards, RAG systems may produce inaccurate information, leak confidential data, or be exploited by malicious actors. Lack of oversight increases the chances of costly mistakes.
Key risks include:
- Data Leakage: AI may unintentionally reveal sensitive or proprietary information.
- Hallucinations and Inaccuracies: Poor retrieval can result in believable but incorrect responses, damaging trust.
- Compliance Violations: Unregulated outputs may breach regulatory standards and result in fines.
- Reputational Damage: Misinformation or biased content can harm your brand and customer relationships.
Key AI Governance Challenges CTOs Will Face in 2026
Implementing effective RAG guardrails introduces several governance challenges that you, as a CTO, must address. The primary challenge is creating a comprehensive risk management framework that can adapt to the dynamic nature of AI. Unlike traditional software, AI models evolve, and their behavior can be unpredictable.
Another significant hurdle is aligning various stakeholders—from data owners and legal teams to AI developers—on a unified governance strategy. Case studies from early adopters show that a lack of clear ownership and accountability can derail even the most well-intentioned AI projects. You need to establish clear roles and responsibilities within your enterprise workflows.
Finally, you’ll need to develop processes for continuous monitoring and auditing. Simply setting up guardrails isn’t enough; you must constantly evaluate their effectiveness and adapt your governance frameworks as new risks emerge and regulations change. This ongoing vigilance is crucial for maintaining long-term compliance and trust.
Balancing Innovation and Safety: Strategic Priorities for CTOs
As CTO, your goal is to drive growth with AI innovation while minimizing risk. Achieving this requires embedding safety into every stage of the innovation process—not treating it as an afterthought—so AI initiatives align with business objectives.
Foster a culture where safety and innovation go hand in hand by:
- Implementing continuous monitoring and robust feedback loops for quick iteration and early issue detection.
- Adopting a risk-based approach: Apply strict controls to high-risk use cases, but allow flexibility in low-risk areas.
- Automating safety checks: Integrate automated guardrails and compliance checks into development pipelines for safer, faster deployment.
- Encouraging cross-functional collaboration: Involve legal, compliance, and security experts with AI teams from the start.
- Prioritizing education and training: Ensure teams have the skills to build and deploy AI responsibly.
From Static Gates to Dynamic Guardrails: Modernizing AI Safety Protocols
The era of static, one-time approvals for AI is over. As we move toward more autonomous systems like agentic AI, our safety protocols must evolve. Traditional, rigid checks are too slow and inflexible for AI that learns and adapts in real time. This is where dynamic guardrails come in.
These modern safety protocols enable real-time monitoring and intervention, ensuring that your AI systems operate within safe boundaries at all times. Let’s explore why old mechanisms fail, how programmable policies offer a better solution, and the path to automating compliance in today’s fluid AI pipelines.
Why Traditional Approval Mechanisms Fail in Agentic Workflows
Traditional approval mechanisms, which often rely on manual reviews and static checklists, are fundamentally incompatible with the speed and complexity of agentic AI. These advanced AI systems can perform multi-step tasks and make decisions autonomously, making pre-deployment approvals quickly obsolete. An agent’s behavior can change based on new data, rendering a one-time check insufficient.
The core issue is that these old methods lack the ability to monitor AI behavior in real time. An agentic AI might encounter a situation that triggers a regulatory or safety concern long after it has been deployed. Without continuous human oversight or an automated system to intervene, you are left with a significant blind spot.
This is why a new paradigm is needed. Instead of relying on a single point of approval, modern AI safety requires a system of continuous validation. This ensures that even as the AI adapts, it remains within the predefined ethical and operational boundaries you have set.
Programmable Policies: Enabling Real-Time, Context-Aware AI Control
To manage modern AI effectively, implement programmable, context-aware policies for real-time control. Unlike static rules, these dynamic policies interpret context and intervene intelligently—essential for reliable AI guardrails in RAG systems.
These policies are coded rules your AI must follow, monitoring behaviors like unauthorized data access or inappropriate content and acting immediately. This automates governance at scale.
For reliable guardrails, a CTO should:
- Define Clear Policies: Establish acceptable AI behavior based on company values and regulations.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select technologies that support programmable policies and real-time monitoring.
- Integrate with CI/CD: Embed policies into development and deployment workflows to keep them active.
- Test and Refine: Routinely test and update policies to ensure effectiveness.
Automating Compliance in Fluid RAG Pipelines
In the fast-paced world of RAG pipelines, manual compliance checks are a bottleneck. The only scalable solution is compliance automation. By embedding automated checks directly into your RAG workflows, you can ensure that every query, retrieval, and response adheres to your governance standards without slowing down the process.
This automation starts with defining your compliance rules as code. These rules can cover everything from data privacy and access controls to content appropriateness and citation requirements. Once defined, these rules are automatically enforced at each stage of the RAG pipeline, providing a layer of continuous monitoring.
The result is a system that is not only compliant by design but also highly efficient. Your teams can focus on innovation, confident that the necessary safety checks are happening automatically in the background. This approach turns compliance from a burdensome task into a seamless part of your AI operations.
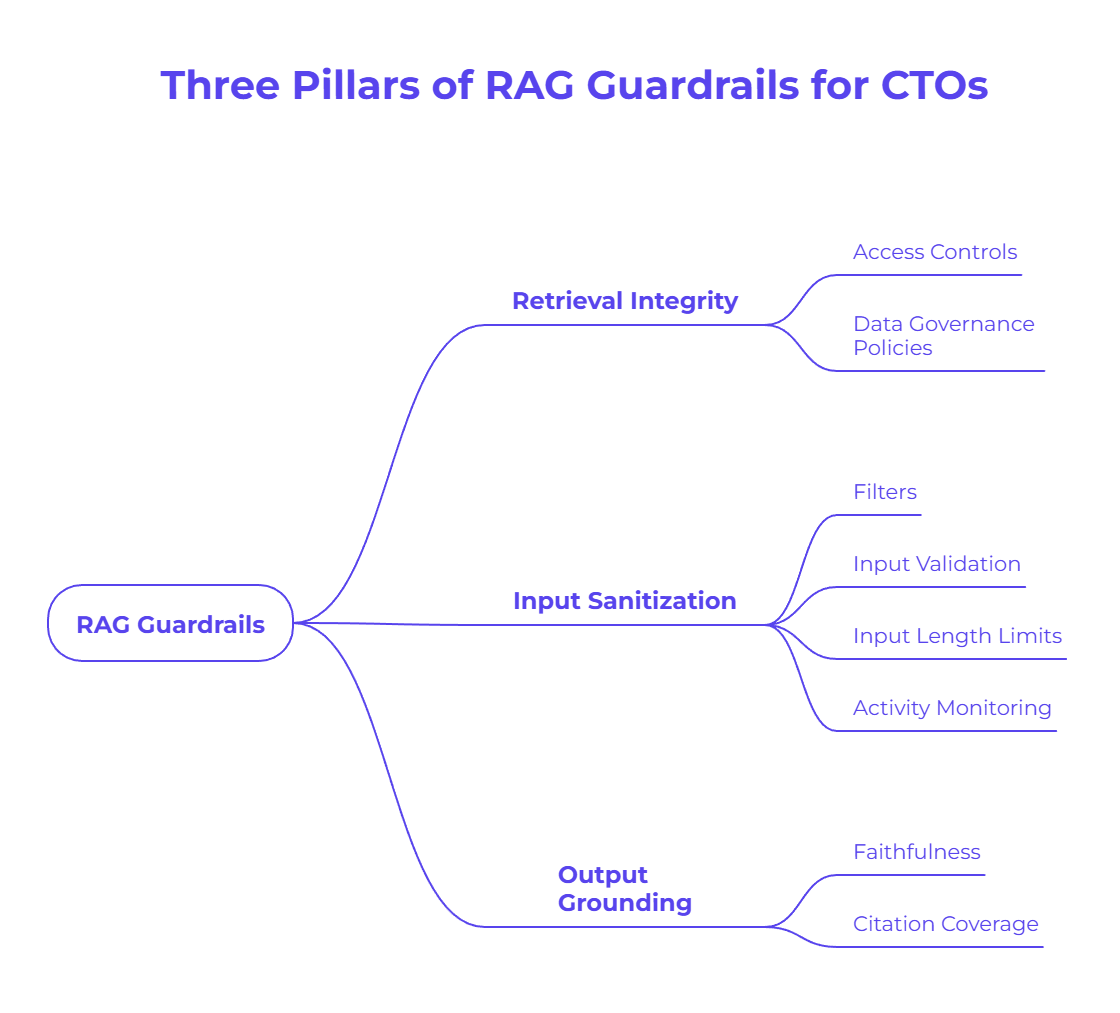
The Three Pillars of RAG Guardrails Every CTO Needs to Know
Building effective AI safety guardrails in 2026 for your RAG systems rests on three core pillars. Mastering these concepts is essential for any CTO looking to deploy secure, reliable, and compliant AI. These best practices form the foundation of a robust RAG governance strategy.
Together, these pillars ensure that your RAG systems are protected from end to end—from the data they access to the answers they generate. We will now explore Retrieval Integrity, Input Sanitization, and Output Grounding in detail to give you a clear roadmap for implementation.
Retrieval Integrity: Ensuring Document Access Rights at the Vector Level
The first pillar, retrieval integrity, is all about controlling what information your RAG system can access. Your AI is only as trustworthy as the data it retrieves, so ensuring secure data access is paramount. This process begins at the foundational level of your vector store, where your documents are indexed and stored.
You must implement strict access controls that mirror your organization’s existing data governance policies. This means a user’s query should only be able to retrieve information that they are explicitly authorized to see. This is especially critical when dealing with proprietary data or sensitive employee and customer information.
By validating permissions at the vector level, you can prevent unauthorized data access before it even happens. This ensures that your RAG system respects data boundaries and maintains the confidentiality of your most valuable information assets, building a foundation of trust and security.
Input Sanitization: Defending Against Adversarial Suffixes and Prompt Injection
Input sanitization is essential for protecting your RAG system from malicious inputs. Attackers use techniques like adversarial suffixes and prompt injection to manipulate AI behavior. Without proper safeguards, your system risks leaking sensitive data or generating harmful content.
Sanitization involves automatically scanning and cleaning all inputs before they reach the language model. This critical security step helps block emerging threats by filtering out adversarial content.
Security research published by OpenAI emphasizes layered defenses for LLM security:
👉 https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/safety-best-practices
To secure your RAG systems:
- Implement Filters: Detect and block known prompt injection techniques and adversarial phrases.
- Validate Input Formats: Accept only expected input formats; reject suspicious entries.
- Limit Input Length: Restrict overly long or complex inputs that could bypass defenses.
- Monitor Activity: Continuously analyze inputs for unusual patterns and flag potential attacks in real time.
Output Grounding: Achieving Faithfulness and Citation Coverage as KPIs
The final pillar, output grounding, ensures AI responses are accurate and verifiable by focusing on two key KPIs: faithfulness and citation coverage.
Faithfulness checks how closely AI outputs match source documents, while citation coverage tracks proper attribution of statements. Prioritizing these KPIs helps prevent hallucinations and builds trust in AI answers.
KPI Overview:
Guardrail Type | Description | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
Faithfulness |
Aligns responses with source documents |
Review for contradictions or fabrications |
Citation Coverage |
Ensures claims are properly cited |
Verify each fact links to a specific source |
Retrieval Integrity: Building Secure and Compliant Data Access in RAG
Ensuring retrieval integrity is the first line of defense in securing your RAG systems. It’s all about making sure that your AI only accesses data it’s supposed to. This requires building a robust access control framework that governs every aspect of the retrieval process, from the initial query to the final selection of documents.A secure retrieval process is foundational to building trust and meeting compliance requirements. Without it, your RAG system could become a source of data leaks. Let’s examine how to validate permissions, prevent data leakage, and choose the right tech stack for granular access control.Validating Permissions at Query and Vector Index Layers
To achieve true retrieval integrity at an enterprise scale, you must validate user permissions at multiple layers of your RAG architecture. It’s not enough to just check permissions at the application level; you need to enforce them at the query and vector index layers as well. This creates a multi-layered defense against unauthorized data access.When a user submits a query, your system should first check their permissions to determine which document collections they are allowed to search. This initial check prevents queries from even being run against restricted data sets. This is your first gatekeeper in the data access workflow.Next, as the system searches the vector index for relevant documents, it should perform another check to ensure that each potential document matches the user’s access rights. This granular, document-level validation ensures that even if a user’s query is broad, the results will be filtered to include only the information they are authorized to see, providing a robust security layerPreventing Data Leakage and Unauthorized Retrieval
A primary goal of your security framework should be to prevent data leakage and unauthorized retrieval. A single instance of a user accessing data they shouldn’t can have severe consequences, from compliance violations to a loss of customer trust. Effective risk management requires a proactive strategy to close these potential security gaps.Your RAG system must be designed with the principle of least privilege in mind. This means that by default, users should have access to nothing, and permissions should only be granted on a need-to-know basis. This approach significantly reduces the risk of accidental or malicious data exposure.Here are some key strategies to prevent unauthorized access:- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on a user’s role within the organization, ensuring they can only access data relevant to their job function.
- Use Metadata for Filtering: Tag documents with metadata indicating their sensitivity level or the teams that can access them, and use these tags to filter retrieval results.
- Redact Sensitive Information: Automatically redact PII and other confidential data from documents before they are indexed or retrieved.
- Log and Audit All Access: Maintain detailed logs of all retrieval activities and regularly audit them to detect and investigate suspicious behavior.
Tech Stack Considerations for Granular Access Control
Choosing the right tech stack is crucial for implementing granular access control in your RAG system. Your technology choices will directly impact your ability to enforce security policies and maintain high retrieval quality. Modern vector databases and search platforms offer increasingly sophisticated features for managing permissions.When evaluating your options, look for a vector database that natively supports metadata filtering and role-based access control. This will make it much easier to build a secure system. Technologies that can combine semantic search with traditional keyword search and metadata filters often provide the best balance of precision and security.Ultimately, your tech stack should allow you to integrate your access control policies seamlessly into the retrieval workflow. The goal is to create a system where security is not a bolt-on feature but an integral part of the architecture. This ensures that your RAG system is both powerful and secure by design.Input Sanitization: Protecting RAG Workflows from Malicious Prompts
Your RAG system is only as secure as the inputs it receives. Malicious actors are constantly probing for weaknesses, using techniques like prompt injection to trick your AI into performing unintended actions. Effective input sanitization is your primary defense against these attacks.This process involves creating a protective barrier that inspects and cleans every prompt before it reaches your large language model. Through continuous monitoring and automated filtering, you can shield your RAG workflows from manipulation. Let’s look at how to detect attacks, implement filters, and integrate the right security tools.Detecting Indirect Prompt Injection Attacks in Real Time
One of the most dangerous threats to language models is indirect prompt injection. This happens when a malicious prompt is hidden in a document your RAG system retrieves. If used, the hidden prompt can make the AI leak data or follow harmful instructions.Real-time detection is essential. Security measures must scan documents for hidden prompts before they reach the model—a critical step for any CTO deploying RAG systems in 2026.To build an effective detection system:- Scan for Instructions: Check document chunks for language resembling commands aimed at the AI.
- Scrutinize External Content: Treat user-generated or external text with extra caution.
- Leverage Heuristics and ML: Use models trained to spot prompt injection patterns.
- Flag and Quarantine: Instantly isolate suspicious content to prevent misuse.
Implementing Automated Filters for Adversarial Inputs
Beyond indirect prompt injection, your AI systems are also vulnerable to direct adversarial inputs, where a user intentionally crafts a prompt to bypass safety controls. Manually reviewing every prompt is impossible at scale, which is why you need to implement automated filters.These filters act as a gatekeeper, analyzing incoming prompts for known attack patterns, malicious code, or attempts to elicit inappropriate content. By automating this process, you can block the vast majority of adversarial inputs before they ever reach your AI model, significantly reducing your system’s attack surface.The key to effective automated filters is to keep them updated. The landscape of adversarial attacks is constantly evolving, so your filters need to be regularly refreshed with new detection rules. This can be achieved through a combination of threat intelligence feeds and machine learning models that learn to identify new attack vectors over time./p>Integrating Security Tools for Continuous Input Monitoring
A strong AI risk management framework requires continuous monitoring of all inputs. Integrating specialized security tools into your RAG pipeline is the most effective way to add this protection. These tools work with automated filters to catch threats that may otherwise go undetected.Advanced features like behavioral analysis can identify unusual user patterns that signal attacks, while detailed logging and alerts give your security team quick visibility and response capabilities.When choosing security tools, consider:- Integration: Ensure easy integration with your RAG architecture without adding significant latency.
- Real-Time Analysis: Tools should analyze inputs instantly to block threats as they occur.
- Customizable Rules: The ability to tailor detection rules to fit your unique security policies and threat models.
- Reporting: Clear dashboards and comprehensive reports for tracking events and proving compliance.
Output Grounding: Guaranteeing Faithful and Verifiable AI Responses
Even with secure data access and sanitized inputs, your job isn’t done. The final and most critical piece of the puzzle is output grounding. This ensures that the responses your enterprise AI generates are accurate, reliable, and directly tied to the source material. Without it, you risk spreading misinformation.Effective output grounding relies on establishing clear metrics like faithfulness and citation coverage to hold your AI accountable. Let’s explore how to set these KPIs, audit your AI’s source attribution, and address the persistent problem of hallucinations.Output grounding enforces hallucination reduction, source attribution, and explainable AI.Enterprises increasingly benchmark against guidance from: These frameworks formalize faithfulness scoring, citation tracing, and auditability.Setting Non-Negotiable KPIs for Faithfulness and Citation Coverage
To ensure your RAG system delivers real business value, you must establish non-negotiable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for the quality of its outputs. The two most important KPIs are faithfulness and citation coverage. These metrics should be at the core of your AI evaluation strategy.Faithfulness measures whether the AI’s response is a true and accurate representation of the information in the retrieved documents. A high faithfulness score means your AI is not making things up or misinterpreting the source material. This is fundamental to building trust.Citation coverage, on the other hand, measures how well the AI attributes its claims to specific sources. A high citation coverage score means users can easily verify the information for themselves, which is crucial in regulated industries or for any high-stakes decision-making. Treating these as mandatory benchmarks transforms them from abstract goals into concrete, measurable objectives.Techniques for Auditing Source Attribution in RAG Outputs
Auditing source attribution ensures AI outputs are grounded in authoritative sources. This involves systematically verifying that responses link correctly to reliable materials, creating clear audit trails.A common method is designing your RAG system to highlight specific sentences or passages from source documents used in responses. This allows reviewers—human or automated—to easily compare outputs with their sources for accuracy.Effective auditing techniques include:- Automated Fact-Checking: Use another AI model to cross-reference claims against sources and flag inconsistencies.
- Human-in-the-Loop Reviews: Have experts periodically review samples for proper attribution, especially in high-stakes cases.
- User Feedback Mechanisms: Let users flag incorrect or missing citations to create a feedback loop.
- Traceability Reporting: Regularly generate reports tracing outputs back to their sources for compliance and transparency.
Addressing Hallucinations and Ensuring Reliable Information Flow
Despite the advantages of RAG, hallucinations—when the AI generates false or nonsensical information—can still occur. Addressing this issue is critical for ensuring a flow of reliable information. The root cause of hallucinations in RAG systems is often poor data quality or the retrieval of irrelevant information.Your first step should be to focus on the quality of your document corpus. Ensure that your data sources are accurate, up-to-date, and well-structured. High-quality data leads to high-quality retrieval, which in turn reduces the likelihood of the AI getting confused and making things up.You should also refine your retrieval system to be more precise. Techniques like hybrid search, which combines keyword and semantic search, can help ensure that the AI is provided with the most relevant information possible. By grounding the AI in highly relevant, high-quality data, you create an environment where hallucinations are far less likely to occur.The Cost of “Shadow AI”: Mitigating Unsanctioned RAG Adoption
While you focus on building sanctioned AI systems, a hidden threat may be growing within your organization: “shadow AI.” This refers to the unsanctioned adoption of unvetted AI tools by employees looking for quick solutions. This trend poses significant security and compliance risks to your enterprise AI strategy.Mitigating shadow AI requires a two-pronged approach: providing better, safer alternatives and educating your teams on the risks. Let’s explore why employees turn to these tools, the strategies to guide them toward sanctioned solutions, and how to build effective training programs.Why Employees Seek Unvetted AI Tools and Associated Risks
Employees often use unvetted AI tools to boost productivity when official options are unavailable or too complex. However, this unauthorized “shadow AI” poses serious risks.The biggest threat is data leakage—pasting sensitive company information into public AI tools means losing control over that data. It could be used to train external models or become exposed in a breach.Key risks of lacking secure, sanctioned AI tools include:- Data Security Breaches: Proprietary and customer data can be exposed.
- Compliance Violations: Using unsanctioned tools may break regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Inaccurate Information: Public AI may provide incorrect or outdated results.
- Intellectual Property Loss: Your company may not own content generated by public AI tools, risking IP issues.
Strategies to Direct Teams Toward Sanctioned, Secure RAG Solutions
The most effective way to combat shadow AI is to provide a superior alternative. If your sanctioned, secure AI solutions are easy to access and meet your employees’ needs, they will have little reason to look elsewhere. This is key to driving enterprise adoption of your official tools.Start by working with business units to understand their needs. What tasks are they trying to accomplish? What are the pain points with their current workflows? Use this business intelligence to develop or procure RAG solutions that are genuinely helpful and integrate seamlessly into their daily work.Your governance frameworks should support, not hinder, productivity. Make the process for accessing and using sanctioned tools as frictionless as possible. By offering powerful, user-friendly, and secure AI solutions, you can naturally guide your teams away from risky public tools and toward a safer, more productive way of working.Building Awareness and Training Programs for Safe AI Use
Technology alone can’t guarantee safe AI use—you must also invest in your people. Building awareness and providing thorough training are vital for effective AI safety. Your team needs to understand both AI’s potential and its risks.Training should cover company AI policies, dangers of unvetted tools, and correct usage of approved solutions. It’s also a chance to build skills for implementing strong guardrails. An informed team is your best defense against AI risks.Key skills and topics to prioritize:- AI Safety Guardrails 2026: Train technical teams to design, implement, and monitor guardrails.
- Data Privacy and Security: Teach everyone how to protect sensitive data when using AI.
- Prompt Engineering Best Practices: Instruct users on crafting effective, safe prompts for optimal RAG system results.
- Critical Thinking and Human Review: Stress that AI supports—not replaces—human judgment; train staff on when and how to review outputs manually.
Beginner’s Guide: How CTOs Can Start Implementing RAG Guardrails
Getting started with AI safety guardrails in 2026 might seem daunting, but you can begin with a clear, step-by-step approach. Implementing these best practices is not just a technical exercise; it’s a strategic initiative that will drive better business outcomes by building trust and reducing risk.This guide will walk you through the initial steps, from assembling the right skills and resources to designing and testing your first guardrails. Let’s break down the process into manageable actions you can take today.What You’ll Need: Skills, Resources, and Toolkits for AI Safety
Before you begin building AI guardrails, you need to assemble the right combination of skills, resources, and tools. A successful implementation depends on having a team with diverse expertise and the right technology to support them. Prioritizing these skills is critical for long-term success.Your team should include not only AI and machine learning engineers but also experts in cybersecurity, data governance, and legal compliance. This cross-functional approach ensures that your guardrails are technically sound, secure, and aligned with regulatory requirements. Ongoing training will be essential to keep these skills sharp.Here are the key skills and resources you’ll need:- Technical Skills: Expertise in large language models, vector databases, prompt engineering, and security engineering.
- Governance Skills: Knowledge of data privacy laws, risk management frameworks, and AI ethics.
- Toolkits: Access to AI safety platforms, monitoring tools, and libraries for implementing programmable policies.
- Resources: A clear budget for technology and training, as well as executive sponsorship to drive the initiative forward.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building RAG Guardrails in Your Organization
Building effective AI guardrails for your RAG deployment is a journey, not a destination. This step-by-step guide provides a structured path to help you get started. By following these stages, you can create a robust risk management framework that evolves with your organization’s needs.
The process begins with understanding your specific context—your regulatory landscape and internal risks. From there, you’ll move into designing and implementing the technical components, and finally, to testing and training. Each step builds on the last, creating a comprehensive safety net for your AI.
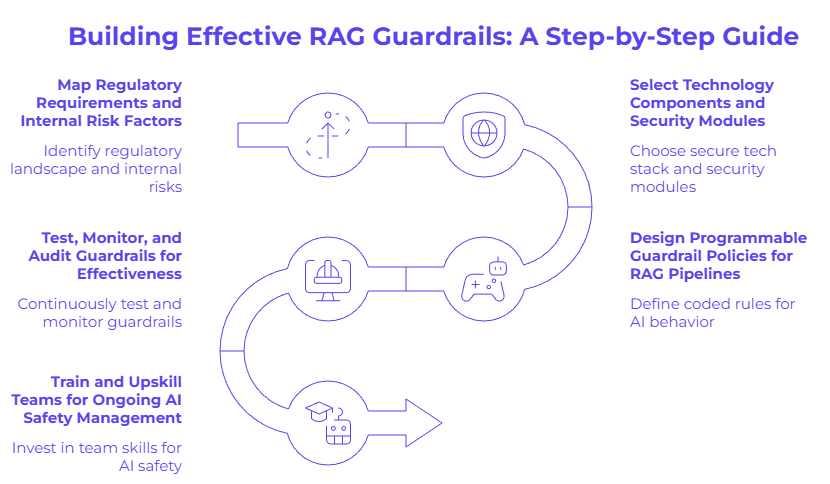
We will now walk through the five key steps in this process: mapping requirements, selecting technologies, designing policies, testing and monitoring, and upskilling your teams. This structured approach will ensure your RAG deployment is both innovative and secure.
Step 1: Map Regulatory Requirements and Internal Risk Factors
The first step in building your AI safety framework is to create a detailed map of your specific landscape. This involves identifying all the regulatory requirements that apply to your industry and region, as well as understanding the unique internal risk factors your organization faces.
Work closely with your legal and compliance teams to create a comprehensive list of all relevant regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or the EU AI Act. Understanding these rules is critical for defining the boundaries within which your AI must operate. This ensures your AI initiatives align with your business objectives from the start.
At the same time, conduct an internal risk assessment. Identify the types of sensitive data your RAG system might access and the potential business impact of an AI-related failure. This combined external and internal view will give you a clear picture of what you need to protect against.
Step 2: Select Technology Components and Security Modules
With a clear understanding of your requirements, the next step is to select the right technology components and security modules for your AI architecture. Your choice of tech stack will have a significant impact on your ability to implement effective guardrails.
Look for a vector database and retrieval system that offer robust, built-in security features, such as metadata filtering and role-based access control. These features will make it much easier to enforce your data access policies. You should also evaluate specialized security modules designed for large language models.
These modules can provide advanced capabilities like real-time prompt injection detection and automated content filtering. By selecting technologies that are designed with security in mind, you can build a RAG system that is secure from the ground up, rather than trying to add security as an afterthought.
Step 3: Design Programmable Guardrail Policies for RAG Pipelines
Now it’s time to translate your requirements into action by designing programmable guardrail policies for your RAG pipelines. These policies are the coded rules that will govern your AI’s behavior in real time. Think of them as the digital “rules of the road” for your AI.
Start by defining policies for the three pillars of RAG safety: retrieval integrity, input sanitization, and output grounding. For retrieval integrity, you might create a policy that blocks any query attempting to access documents tagged as “confidential” from an unauthorized user. This is a fundamental guardrail.
For input sanitization, you could design a policy that automatically rejects any prompt containing known adversarial phrases. For output grounding, a policy could flag any response that fails to cite a source. These programmable policies are the core of a dynamic and responsive safety system.
Step 4: Test, Monitor, and Audit Guardrails for Effectiveness
Implementing guardrails is not a one-and-done task. The fourth step is to continuously test, monitor, and audit your guardrails to ensure they are effective. The AI landscape is always changing, and your safety measures must adapt to keep pace.
Establish a regular testing schedule to probe your guardrails for weaknesses. This can involve “red teaming” exercises where a dedicated team tries to bypass your safety controls. The insights gained from these tests are invaluable for strengthening your defenses. Implement continuous monitoring to track key safety metrics and create robust feedback loops.
You should also set up automated systems to create detailed audit trails of your AI’s behavior. These logs are essential for investigating any incidents and for demonstrating compliance to regulators. This cycle of testing, monitoring, and auditing creates a feedback loop that allows you to constantly improve your AI safety posture.
Step 5: Train and Upskill Teams for Ongoing AI Safety Management
The final step is to invest in your people. Your AI safety framework is only as strong as the team that manages it. Ongoing training and upskilling are crucial for ensuring that your team has the skills needed to manage AI safety effectively in the long term.
As a CTO, you should prioritize building a team with a diverse set of skills that covers both the technical and governance aspects of AI safety. This investment in team skills will pay dividends by creating a culture of responsible innovation and reducing the risk of costly AI failures.
Key skills and training areas to prioritize include:
- AI Security: Training on the latest adversarial attack techniques and defensive measures.
- Data Governance: Deep knowledge of data privacy regulations and best practices for managing sensitive data.
- Ethical AI: Understanding the principles of fairness, accountability, and transparency in AI.
- Monitoring and Auditing: The ability to interpret AI monitoring data and conduct effective audits of AI systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing robust AI safety guardrails is essential for CTOs navigating the evolving landscape of Retrieval-Augmented Generation, enterprise LLMs, and AI compliance in 2026 and beyond.
By operationalizing the three pillars—retrieval integrity, input sanitization, and output grounding—you can deploy AI that is not only powerful but also transparent, auditable, and secure.
As regulations tighten and the risks of unverified tools rise, now is the time to embed AI governance, continuous monitoring, and responsible AI engineering into your core strategy.
Contents
Frequently Asked Questions
Most frequent questions and answers
CTOs should budget for the cost of specialized security tools, ongoing training for their teams, and potentially hiring staff with expertise in AI safety. While there is an upfront investment, implementing AI safety guardrails in 2026 for your RAG systems ultimately delivers business value by reducing compliance risks and building trust in your enterprise AI.
Enterprises can measure effectiveness by tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) like faithfulness and citation coverage. Other metrics include the rate of blocked adversarial inputs and the number of data access violations prevented. Establishing user feedback loops also provides qualitative data on the performance of your enterprise AI and helps improve business outcomes.
CTOs should prioritize a mix of skills. This includes technical expertise in AI security and vector databases, as well as governance knowledge of data privacy and risk management. Investing in training for continuous monitoring and ethical AI principles is also critical for building and maintaining effective AI guardrails.
CTOs ensure compliance by integrating AI safety into their governance frameworks. This involves mapping regulatory requirements, implementing programmable policies, and maintaining detailed audit trails of AI behavior. A proactive approach, focusing on transparency and accountability, is key to meeting compliance standards for RAG models by 2026.



